As a small business owner, you know your financial information is essential to the success of your company. But protecting that sensitive data isn’t always easy – especially with more sophisticated cyber-attacks cropping up every day. Keeping your finances safe requires effort and vigilance on your part, but it doesn’t have to be an overwhelming task.
From online banking to mobile payments, individuals and businesses rely more on digital financial services than ever before. However, this growing reliance on technology also increases the risk of financial fraud and cybercrime. To protect sensitive financial information from unauthorized access and theft, it is essential to take proactive steps to secure your data.
In this blog article, we’ll discuss 3 easy methods you can use to protect financial data from prying eyes and malicious attackers, and ensuring peace of mind for both you and your customers.
1. Masking
Masking is a powerful technique that can help protect sensitive financial data for businesses. In essence, masking involves replacing sensitive data with a substitute. For example, a business might use masking to replace real social security or bank account information with masked versions that still appear real but are not actual account numbers. Let’s say, instead of 123-45-6789, you mask it to read ***-**-6789. Masking can help protect against data breaches or unauthorized access to sensitive financial information.
Masking is particularly useful for businesses that need to share sensitive financial data with third-party service providers, such as payment processors or accounting firms. By masking the data before sharing it, businesses can minimize the risk of the data being intercepted or misused.
In addition to protecting against data breaches, masking can also help businesses comply with regulatory requirements related to data privacy and security. For example, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) requires businesses to protect credit card data through the use of data masking, encryption, or tokenization.
2. Tokenization
Tokenization is another effective way for businesses to protect their sensitive financial data. Similar to masking, tokenization involves replacing sensitive data with a substitute. In tokenization, the substitute is a unique and random token with no intrinsic value or meaning. This token can be used to represent the original data in secure systems and processes while the actual data is stored in a separate, highly secure environment.
For example, a business might use tokenization to replace a customer’s credit card number with a token that can be used to charge the card for future transactions. This way, the credit card number is never stored in the business’s systems or databases, reducing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access.
Tokenization has several advantages over other methods of data protection. Since tokens have no intrinsic value, they are useless to hackers or other unauthorized users who may gain access to them. In addition, tokenization can be used for a wide range of sensitive data, including bank account numbers, social security numbers, and other personally identifiable information.
Tokenization can also help businesses comply with regulatory requirements related to data privacy and security, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
3. Encryption
Encryption is another important way for businesses to protect their sensitive financial data. Encryption involves converting data into a secret code that can only be read with a corresponding key or password. This can help protect financial data from unauthorized access or theft, as the encrypted data is meaningless without the key or password needed to decrypt it.
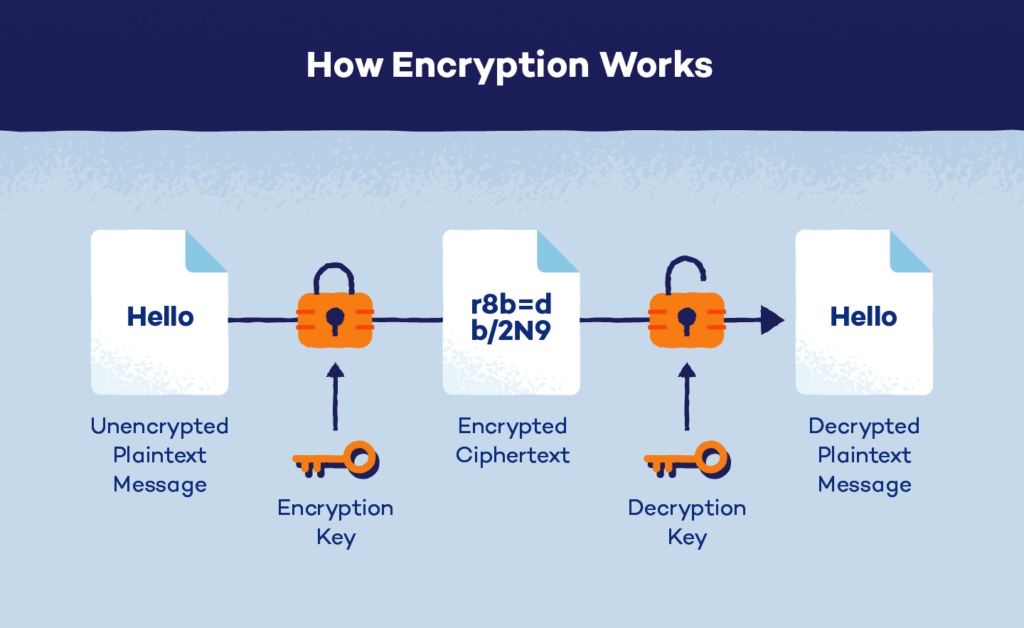
Above image courtesy https://www.pandasecurity.com/en/mediacenter/security/what-is-encryption/
For example, a business might use encryption to protect customer credit card information when it is stored or transmitted. The credit card number is encrypted and can only be decrypted with the corresponding key or password, which is kept securely by the business.
Encryption has several advantages over other methods of data protection. Unlike masking or tokenization, which use substitutes to protect sensitive data, encryption provides a high-security level by scrambling the data itself. This makes it much more difficult for hackers or other unauthorized users to access or steal the data.
The (Encrypted) Bottom Line
Masking, tokenization and encryption are three powerful tools that businesses can use to secure their sensitive financial data from theft. Businesses should have a strong security policy as the first step in protecting their data. As companies embrace the transition to digital banking and other on-line services, they must also implement security measures that will protect customer and business information from malicious hackers. Keeping track of changes in technology is important for businesses, especially when it comes to protecting customer data.
Primary steps like masked user names and encryption of confidential messages can effectively protect organizations’ money and data by preventing malicious access. Additionally, tokenized payments offer an extra layer of protection against fraud or abuse by hiding customer account details from unauthorized people or systems. By taking proactive steps to secure sensitive information, businesses can build trust with customers and partners and reduce the risk of financial fraud or cybercrime.


