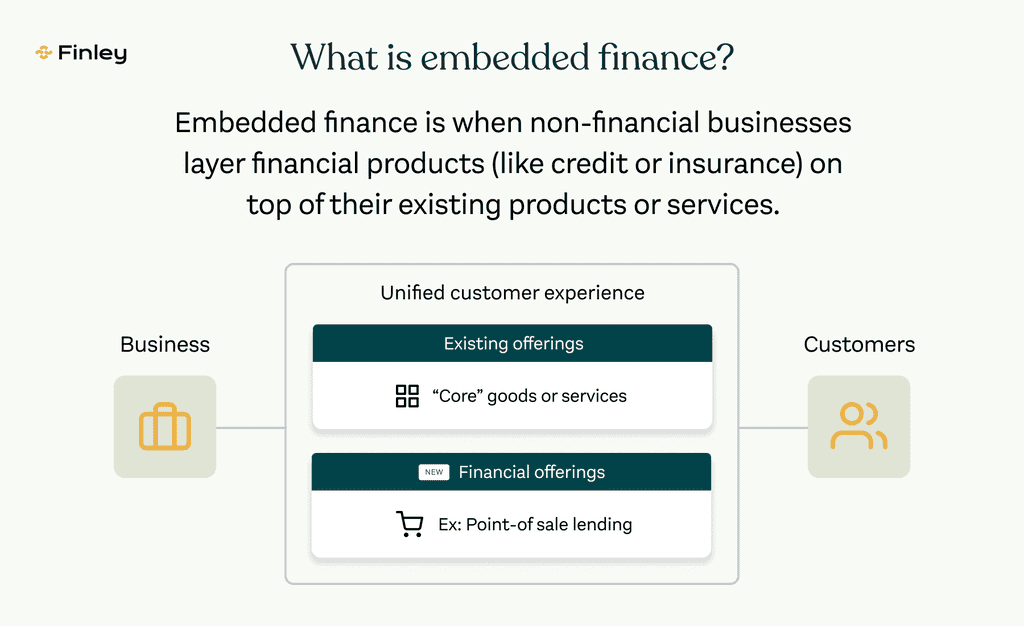
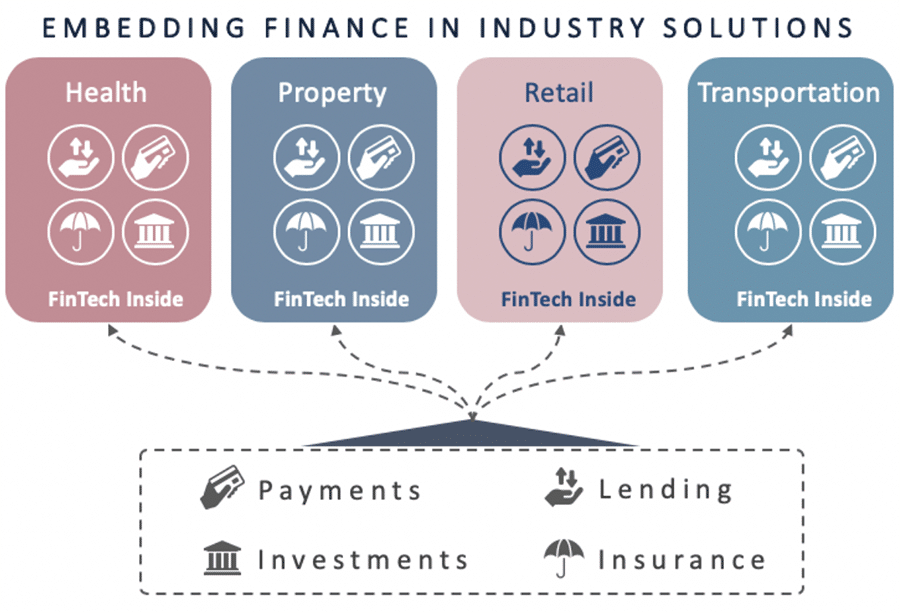
The rise of the API in banking and payments is bringing embedded finance to all kinds of financial services use cases. With APIs, companies (besides banks) can include financial services offerings in their digital apps or products. Ultimately, this leads to benefits for customers, businesses, and even banks. So what exactly are the benefits of the API and embedded finance?
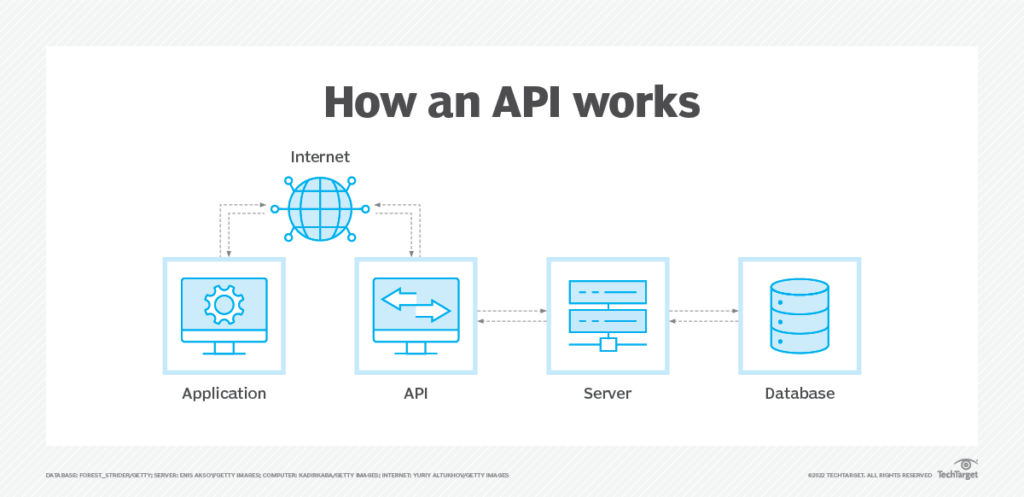
What is an API?
API stands for application programming interface, and is a way for two or more computers or computer programs to “talk” with each other. An API allows different programs and companies to work together in the background to provide the end customer with a streamlined experience once permission is given.
APIs are powerful because you can set them up once with an easy process. Once that process is complete, the API doesn’t have to be set up again.
Benefits of APIs in Banking
With APIs, a financial service or independent payment provider accesses user data through the user’s bank account (with consent). This helps third-party companies create products around banking services and create value for their end-users.
Customers can also perform transactions within apps instead of going through their bank accounts. If you ever used Stripe to connect your bank with another application, you benefited from an API.
Benefits of APIs for Consumers
The biggest benefit of APIs to consumers is speed and convenience. For example, consumers may use a budgeting app to track their personal finances. By integrating their app with their bank using an API, they don’t have to manually import their banking transactions.
Instead, their transactions automatically get pulled from their bank, credit card companies, savings accounts, and so on via the API. The consumer sets this up once and gets an automatic, monthly download of transactions until they turn this process off.
Benefits of APIs for Businesses
With an API that connects to various financial service providers, the budgeting app mentioned in the example above can reduce a major pain point for its customers. This isn’t possible without an API, and makes the app valuable and marketable by reducing friction for the end user. It also makes the product faster and easier to use.
Business owners can also benefit from APIs when managing their business. For example, rather than logging in and out of various platforms, applications allow business owners to connect to multiple banks using APIs.
Benefits of APIs for Banks
Banks can also benefit from APIs because they can offer or recommend new products and services without having to create them themselves. For example, they can recommend budgeting or financial software to their clients that a third party created.
With the API integration, the bank’s data can be leveraged by the third party to create a business solution that the bank wouldn’t have been able to provide itself. At the end of the day, the bank, the consumer, and the third-party app creator all reap the benefits of API and embedded finance.


