Providing a great small business employee compensation plan and benefits package can make a huge difference when it comes to attracting and retaining talented employees for your business. From state minimum wage requirements to benefits packages, here’s what you need to know to get going.
Start Here: Small Business Employee Compensation
From developing a pay scale for each position to sorting through insurance benefits, you have a lot to consider as a small business owner.
For example, you’ll want to find an easy, streamlined way of issuing paychecks so you aren’t wasting precious time with routine tasks. You’ll need to comply with your local regulations. Finally, you’ll want to put together a benefits package that brings top talent into your organization.
If you’re feeling overwhelmed and don’t know where to start with employee compensation, these are the best places to begin.
State Minimum Wage: What You Should Be Paying Your Employees
Minimum wage requirements are helpful because they give you a non-negotiable place to start as you are determining a pay scale for your employees.
Many states across the country have a minimum wage of $7.25. This includes Texas, Idaho, Utah, and many more. On the other end of the spectrum, states like California and Oregon require $15 and $13.50 respectively.
The United States Department of Labor provides an overview of state minimum wage requirements. Here, you can research the most up-to-date state minimum wage requirements in your state.
Note also that your city may require you to pay a higher minimum wage than your state. This is particularly common in big cities where the cost of living is much higher than the rest of the state. For example, the minimum wage in Seattle, Washington is $15.45, while the state as a whole comes in at just $11.50.
You can use the interactive map from the Economic Policy Institute to find your state minimum wages, as well as city-specific laws and tipped wage adjustments.
Designing A Small Business Employee Compensation Plan
Once you determine the minimum wage requirements in your area, you need to come up with an employee compensation plan. What is right for one company may not make sense for another. For this reason, it’s important to consider the goals and needs of your company.
The most common types of compensation plans include:
- A straight salary determined for each job title or position (may include a range with a minimum and maximum to accommodate for promotions)
- Salary plus commission for employees who are encouraged to make sales and reach goals, but still receive base pay
- Commission-only plans for sales people who must perform in order to get paid
From your previous experience, you probably already know what type of employee compensation plan is standard in your industry. For example, while a retail shop may offer a commission to entice sales employees, this same model probably wouldn’t work for a small coffee shop.
If you’re not sure, don’t be afraid to ask your industry mentors and resources to find out what typically works best in your particular industry. It will help you make sure what you’re offering is competitive and on the right track.
57 Sales Tips That Actually Work!
From the President of PaySimple to You: The Small Business Sales Guide
Click here to access the FREE guide
How Do You Calculate Compensation?
There is no exact science to calculating employee compensation, but again, research can help you determine the median salary of people working in the same or similar roles at other companies.
First, decide on the maximum amount you’re able to pay for each position. Consider what rates you’re comfortable with according to your budget, as well as the value each particular role holds in your company. If it’s an integral role, you may raise the employee compensation rate to be able to hire that truly great employee.
Next, you need to do a little homework to figure out a minimum so that you remain competitive. That’s where a little research goes a long way. Both PayScale and GlassDoor also offer free online calculators for calculating median salary ranges for positions in your industry and location.
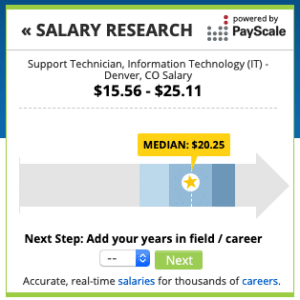
For example, if you were looking for IT support, you could use PayScale to search for the median employee compensation rate for that position in your area. A quick search shows that most IT support technicians make around $20/hour, but could go up to $25/hour with the right skills and experience. Additionally, you can talk to your local industry mentors and professional networking groups for advice on appropriate and competitive employee compensation for a certain role.
How To Offer Benefits As A Small Business
There are a few employee benefits that you’re generally required to provide by federal law:
- Social Security taxes paid at the same rate as your employees
- Workers’ compensation through a commercial carrier, state program, or self-insured basis
- Leave benefits, as stipulated in the Family and Leave Medical Act (FMLA)
Other benefits vary from state to state. For example, disability pay is required in California, Hawaii, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, and Puerto Rico. You may also have to register for unemployment insurance with your state workforce agency.
If you have less than 50 employees, health insurance benefits are optional. Even larger organizations can forgo health insurance, but they may face tax penalties. With that being said, offering health insurance benefits can help you attract and retain better employees. If you decide to go this route, you will still need to follow various guideline outlined by the U.S. Department of Labor and you may also have to extend the option of COBRA (Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act) benefits to employees who are terminated or laid off.
Depending on your business, you may also want to consider offering employee benefits in the form of discounts. For example, it’s common for retail stores to offer employees a certain percentage off products in store. If you own a small restaurant, maybe you offer your employees one free meal per shift. Universities may offer reduced tuition for employees and their families, while larger publicly shared businesses can provide employees with stock benefits.
Together, these can be an added incentive for a potential employee, especially if they’re already a fan of your business.
How Do Small Businesses Pay Employees?
The final piece of the employee compensation puzzle is how you’ll actually issue payments to your employees. You have a few options, but ACH transactions and eChecks are among the most popular methods today.
ACH (Automated Clearing House) is a fast, secure, and cost-effective way to transfer funds between bank accounts. ACH transactions are an easy, modern alternative to handing out paper checks.
An eCheck is an electronic check. It’s just like an old-fashioned paper check, but the money is transferred between accounts electronically. Both of these options are typically considered more convenient for both you and your employees.
Learn More About Employee Compensation
If you’re interested in additional resources on better ways to recruit, onboard, and manage reliable employees, we can help.
Access our on-demand webinar “Better Employee Management Through Automation” for tech-powered tips to scale up your hiring processes, manage your staff, and automate your payment systems.
Start a 14 day Free Trial and streamline your business with PaySimple:


