Traditional financial systems have often been rigid and slow to adapt in our fast-moving world, causing inefficiencies and challenges for businesses and individuals. Luckily, financial technology (FinTech), an innovative intersection of finance and technology, has been at the forefront of disrupting the traditional financial landscape, responding to the changing needs and demands of the modern marketplace. In this post, we’ll discuss 6 technologies shaping the FinTech world and how these technologies will affect your businesses.
Six Areas Shaping the Future of Fintech
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI), the simulation of human intelligence within machines using complex algorithms and computational capabilities, has transformed the financial sector. Its fintech applications are multifaceted, from automating routine tasks such as data entry and processing, reconciliation, and basic decision-making, to enhancing customer service through natural language processing and machine learning.
For example, AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide 24/7 support and personalized interactions, creating unprecedented customer engagement. In addition, AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of transactional data to identify abnormal patterns, reduce fraud risks, and offer tailored financial advice, product recommendations, and investment strategies.
AI’s applications can be particularly beneficial for small businesses, often constrained by limited resources. Businesses can increase efficiency by automating routine tasks, reducing manual effort, and allowing a focus on strategic initiatives. Businesses can reduce costs because AI can perform tasks at a fraction of the cost of human labor. This enables small businesses to allocate resources to other crucial areas, enhancing overall performance and competitiveness. Additionally, informed decision-making, supported by AI’s data-driven insights, helps small businesses in areas like marketing, pricing, inventory management, and investments.
Finally, AI’s ability to safeguard against fraudulent activities minimizes potential financial losses, providing an essential security layer for small businesses.
2. Blockchain
Blockchain technology, as a decentralized ledger system, represents a groundbreaking advancement in the field of finance, poised to redefine how transactions are conducted and recorded. Unlike traditional centralized databases managed by a single entity, blockchain operates on a network of computers, each holding a copy of the ledger. This structure ensures the integrity and transparency of transactions, rendering alterations virtually impossible without the consensus of the entire network.
The application of blockchain is multifaceted, and its impact is felt across various financial industry sectors. In payment systems, blockchain can revolutionize how money is transferred and received, bypassing traditional banks and financial institutions. This can lead to quicker and more cost-effective transactions, especially in the case of international payments.
In asset management, blockchain provides an unalterable, time-stamped record of asset ownership and transactions, reducing errors and the risk of fraud. Additionally, compliance tracking becomes more streamlined with blockchain, as regulators can access transparent and immutable data in real time.
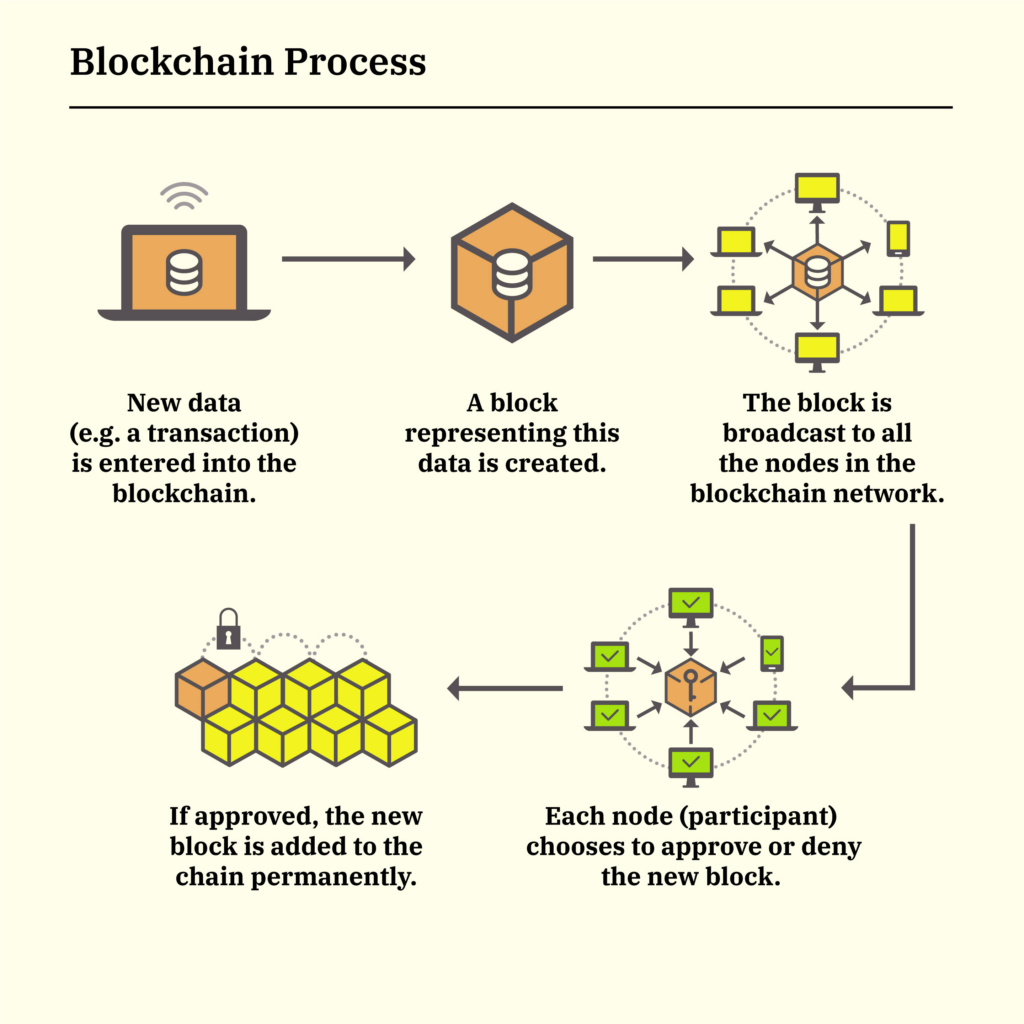
Image courtesy: https://money.com/what-is-blockchain/
For small businesses, the benefits of implementing blockchain technology are substantial. First and foremost, blockchain fosters trust among parties. Since the record of transactions is transparent and cannot be altered unilaterally, all participants in the network can have confidence in the accuracy and integrity of the information. This trust is especially crucial in relationships between small businesses and their stakeholders, including suppliers, customers, and financial partners.
Furthermore, by eliminating intermediaries, blockchain can help reduce costs. Traditional financial transactions often involve multiple middlemen, each adding layers of complexity and fees. Blockchain’s peer-to-peer nature simplifies this process, making transactions more direct and efficient.
3. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the connectivity of physical devices, allowing them to collect and exchange data. In finance, IoT offers benefits like real-time tracking, automation, and enhanced data analysis. These functionalities can streamline processes, increase efficiency, and provide deeper insights.
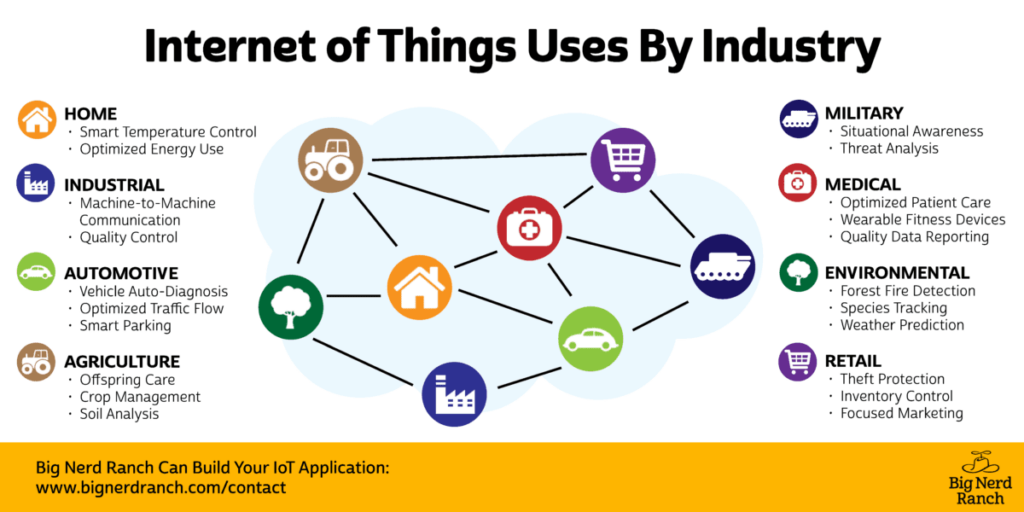
Image courtesy: https://bignerdranch.com/blog/what-the-internet-of-things-means-for-your-business/
Small businesses, in particular, stand to gain significantly from IoT. Improved inventory management through real-time monitoring, more accessible expense tracking through consolidated data, and enhanced customer engagement are some areas where IoT’s impact is pronounced. An example is the use of IoT-enabled Point of Sale (POS) systems, which not only process transactions but also capture valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences. This information can enable businesses to personalize offerings and strengthen customer relationships.
4. Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based service model transforming how businesses access and utilize software. Rather than investing in expensive hardware and managing software on local servers, SaaS allows businesses to access software applications over the internet. This model fosters an environment of flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, shifting from a capital expenditure approach to an operational expenditure model.
The benefits of SaaS are particularly relevant for small businesses, for whom accessibility, cost efficiency, and adaptability are often key priorities. SaaS solutions require no significant upfront investment in hardware or software licenses, thereby minimizing initial costs. The pay-as-you-go pricing model further ensures that businesses only pay for what they use, allowing them to scale their services as needed.
This scalability is instrumental in helping small businesses adapt to changing market dynamics and business needs without being burdened by inflexible technological infrastructure.
5. Open-Source and Serverless Platforms
Open-source platforms and serverless architectures are technologies reshaping how businesses approach software development and deployment. Open-source platforms allow collaboration and customization by providing access to the source code. This access enables businesses to modify, improve, and adapt the software to meet specific needs, encouraging innovation and flexibility.
In contrast, serverless architectures enable applications to run without dedicated servers, relying on cloud providers to manage server space, thereby reducing the overhead and complexity of server management.
For small businesses, these technologies offer distinct advantages. Open-source platforms can promote agility, allowing them to adapt software quickly to changing market conditions or unique business requirements. The collaborative nature of open source also fosters a community-driven approach to innovation, tapping into collective expertise. Additionally, serverless architectures reduce costs by eliminating the need for continuous server management and maintenance.
6. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) lending is an innovative financial model that has dramatically altered the lending landscape. By connecting borrowers directly with individual lenders through online platforms, P2P lending bypasses traditional financial institutions, creating a more streamlined and accessible process.
This approach offers distinct benefits for small businesses, who often face challenges securing financing from conventional sources. Traditional banks usually have stringent requirements and lengthy approval processes, which might not align with the fast-paced and dynamic needs of small businesses. P2P lending, on the other hand, provides quicker, more flexible financing options. The online platforms facilitating P2P lending often have simplified application processes and quicker response times, allowing small businesses to access the necessary funds without unnecessary delays.
Moreover, P2P lending often presents more favorable terms for borrowers. Since the model operates with reduced overhead and intermediaries, the cost savings can translate into lower interest rates or more tailored repayment schedules. This financial advantage is particularly appealing for small businesses looking to secure a loan for expansion, as illustrated in the example of a small business utilizing a P2P lending platform to obtain a loan on more favorable terms than those offered by conventional banks.
The Bottom Line
The FinTech environment is undoubtedly a dynamic and revolutionary field, offering unprecedented opportunities for small businesses to enhance their operational efficiency and competitiveness. The convergence of technologies such as AI, blockchain, IoT, SaaS, open-source and serverless platforms, and P2P lending is not merely a trend but a transformative force that will continue to reshape the financial and business landscapes.
The future FinTech environment will be characterized by greater personalization, decentralization, and democratization of financial services. By embracing these technological advancements, businesses can adapt and thrive in this ever-evolving marketplace. Leveraging FinTech will be integral to driving growth, innovation, and the entrepreneurial spirit that fuels our global economy.